Uveitis
An intraocular inflammation affecting the uvea, made up of the iris, the ciliary body and the choroid.
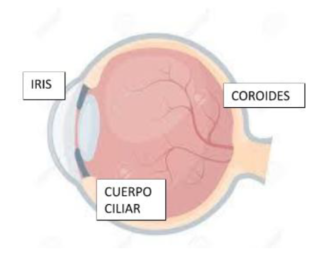
It can be:
Anterior
Affects the iris and the ciliary body
Medium
Affects the pars plana (part of the ciliary body)
Posterior
Compromises the choroid and the retina
Total uveitis
The whole eye is swollen
Potential causes:
Infectious
Caused by a virus (e.g., herpes), bacteria (e.g., tuberculosis), mycosis (e.g., candida) or parasites (e.g., toxoplasmosis).
Immunological/inflammatory
Generally associated with pathologies such as Behcet’s Disease, vasculitis or eye-specific disorders.
Trauma
After a bruise.
Uveitis (or iritis) presents with eye pain, photophobia, visual sharpness impairment, mostly eye redness and it is sometimes linked to headaches. It can be acute and may reappear with recurrences or become chronic.
It is diagnosed in the ophthalmologist’s office and by way of tests to find out the cause. It is treated with eye drops or local applications. Where necessary, systemic oral treatment is provided with anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics and/or antiviral drugs, as per the disease-causing agent. Upon the onset of symptoms, it is important to have periodic checks and visits to the physician.